Lecture - Changing Fashion Landscapes
Changing Fashion Landscapes
Ethics:
- Exploitative labour
- Environmental damage
- Chemicals
- Waste
- Animal cruelty
Circular Economy:
- A circular economy is an alternative to a traditional linear economy (make, use, dispose) in which we keep resources in use for as long as possible, extract the maximum value from them whilst in use then recover and regenerate products and materials at the end of each service life. (wrap, 2018)
Sustainability
Closed loop system:
Examples of ‘closed loop’ company strategies:
- Levi’s and H&M
Examples of brands slower to adopt closed loop
- Primary
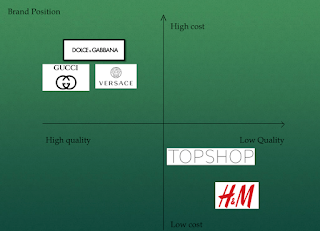
Luxury brands;
- Farming animals for fur
- Difficult to trace some supply chains/ accountability for production
Impacts;
- Sustainability
- Climate
- Depletion of natural resources (animal, habitat, water, and so on )
Eco Fashion
- Fashion sustainability
- People tree
- Patagonia
- UNMADE: niche knitwear - consumer can produce their own product
- Traid
- Oxfam hub Batley; online vintage
Counterfeit goods
- Luxury market
- Countries and counterfeit
- Creates problems with sales, profit and the kudos of the brands in question
- Further promotes unethical practice, hidden manufacture of goods
Social responsibility
- What we consume
- Why we consume
- What forms our consumer patterns
- Who is responsible for increased consumption
- Our understanding of product use and where product goes
- How our actions impact on others (links back to ethics )
Generational Shifts
- Different consumers, consume in different ways
- Generation X; largely bricks and mortar (high street ) with some online consumption
- Generation Y; largely online, with some bricks and mortar consumption
- Generation Z; born into the digital age
- Methods of marketing to consumers are continually shifting, due to the complex nature of the cross generational experience of interacting with identifying product.
Marketing methodologies
Bricks and mortar type institutions; for example: John Lewis
- Television
- Loyalty cards/ data collection
- Long routes to identifying and engaging their customers
Online
- Uses cross sectional marketing/ advertising
- Social media
- Some terrestrial TV advertising (example: BooHoo.com )
- posters/ digital bill boards/ taxi’s (again in the case of BooHoo.com)
- Fast fashion social media and cascade
High street retailers engaging the customer
- Both digitally and psychically
- Topshop; online offers as well as high street lock ins for students for example
Generation X
- Bought up through the era of ‘physical’ shopping experience
- Department store
- High street brands
- Have a tendency to brand loyalty and still attach ‘value’ to the cost of an item
- Tend to reflect personal status through
Gen Y
- Cross over generation
- Still brick and mortar but also digital
Gen Z
- Born through the age of digital technology
- Easily navigate through Digital
Consumer shifts
- Shift to online shopping
- Comparing and contrasting product online
- Sourcing best price on line comparison
- Social media ; provides a platform to display product choice
- Online shopping has seen he shift of consuming fast fashion through faster cycles; sees the product buy the product move onto the next look
- There used to be bi annual collections however now there is mire pressure to get mire out poor year
Impact of online versus high street
High street
- Same price diff stores
- Increasingly less differentiation in product
- Prices higher as they pas for space
- The act of going shopping isn’t con Vincent as you have to pay for parking etc
- People are busy
Online
- More convenient
- Diverse choice
- Drill down on product and find the cheesiest price more choice regarding size
- The opportunity to source garments that are less likely to be worn by others
Can the high street fight back
- High street Strategies to revive footfall
- Examples
- Burberry - physical meets digital
- Adidas - working on interactive experience in store
Where does this leave us ?
Now:
- Globalisation
- Materials
- Labour
- Sourced products at low cost
- Industrialised methods of growing crops
- Habitat and environmental destruction
- What does the fashion future hold.
Futures:
- Further digitalisation
- Ache product
- Embedding of technologies
- Digitalisation in fashion print/ textiles
- 3d printed product (one off)
- Biometrics
- Textiles grown from organisms
- A more sustainable, design led fashion future?


Comments
Post a Comment