Consumer behaviour, target positioning and Marketing of the brand/ fashion cycle
Consumer behaviour, target positioning and marketing of the brand/ fashion cycle lecture
Monday 21st Jan
What is consumer behaviour?
- Individuals of groups select, purchase use of dispose of products, where do they end up?
Maslow's hierarchy of needs
- Self-actualisation needs: The desire for self fulfilment in achieving whatever someone can
- Esteem and status: striving to achieve a high standing in relation to other people
- Social needs: we need social experience and desire products and services that facilitate social exchange
- Safety needs: protection from the unpredictable happening in life
- Physiological needs : the fundaments of survival
Self esteem Richins 1993:
Marketers use attractive models for a social comparison sonf process where young female consumers compare themselves and feel inadequate against them.
What this model doesn’t really account for the influence of others for example how does family affect the behaviour and consumption?
Diverse and changing markets:
Most fashion marketers try to attract several market segments at once, e.g. GAP sells to men, women and children. Consumer buying behaviours don’t remain the same, changes in economic or social conditions can affect the consumers choices.
Segmenting a market
Market segmentation is a way of analysing a market by categorising their specific characteristics
Specific characteristics include:
- Demographics - are statistics that describe a population in terms of personal characteristics such as age, gender, income, ethnic, education, religion, lifestyle
- Psychographics - are studies of consumers based on silva and phycological characteristics such as attitudes, interests and opinions
- Geographic - are statistics about where people live
- Behaviouristic/ usage - are statistics about consumers based on their knowledge, attitudes, use, or response to a product
- Situation
- Geodemographic
Purchase occasion - identifies the instance when a consumer might use a product
Product benefits: identifies the benefits that consumers desire in a fashion product or service (stain resistant or wrinkle free)
Usage levels and commitment - identifies how often they use a product and their loyalty to purchasing it (will you buy a replacement)
Geodemographic segmentation - hybrid segmentation, you are where you live (financial means, tastes, preferences, lifestyle and consumption habits.)
Targeting:
The next step is targeting, in which marketers evaluate each potential segment and decide upon which groups of customers they will invest marketing resources
- Selected groups are known as target markets
- How is technology making it easier for fashion firms to target potential customers? ( social media )
Brand positioning statement
Brand positioning is defined as the conceptual place you want to own the target consumers mind - the benefits you want them to think of when they think of your brand. An effective brand positioning strategy will maximise customer relevancy and competitive distinctiveness in maximising brand value.
When doing your research to inform a brand positioning project you must b e able to answer the following questions:
- What does the brand community currently believe or value about this brand?
- What might the brand community believe or value about the brand in the future
- What does the organisation currently claim about the brand?
- What would the organisation like the brand to become down the road?
The final step … positioning
How do you want to be seen in the market place? What is your key competitive advantage? What do you want to highlight?
Product differentiation e.g. the lynx affect will make you more sexually attractive towards women
Service differentiation e.g. kia offer a 7 year warranty
Personnel differentiation e.g. apple geniuses.
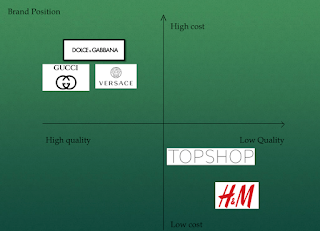
What is market mapping?
The market map illustrates the range of positions that a product can take in a market based on two dimensions that are important to customers
Possible dimensions:
- Low price/ high price
- Basic quality / high quality
- Low volume/ high volume
- necessity/ luxury
- Light / heavy
- Simple / complex
- Unhealthy/ healthy
- Low tech/ high tech
You can use maps to see gaps in the market and see where the proposed brand can fit in the market
Product life cycle
The fashion cycle
Fashion cycle: the ongoing introduction, rise, peak, decline, and obsolescence in popularity of specific styles or shapes
All styles that come into fashion rotate through the fashion cycle
Stage 1 - introduction stage
- The first stage of the fashion cycle is when new styles colours textures and fabrics are introduced.
- The new style may be accepted by a small number of people called fashion leaders
- Promotional activities include fashion shows and advertising of high fashion magazines
- Fashions are produced in small quantities in his prices
- Retail buyers purchase limited numbers to see if the style will be accepted
Stage 2 - growth/ rise
- The second stage of the fashion cycle when consumer interests grows and the fashion becomes more readily accepted by consumers
- Mass production brings down the price of the fashion which results in more sales
- Styles are manufactured in less expensive materials and in lower quality construction than the original style
- Promotional efforts are increased in high fashion magazines to heighten consumer awareness
- Retail buyers order items in quantity
Stage 3 - maturity/ peak
- The third stage of the fashion cycle during which a style is at its height of popularity
- The fashion is demanded by almost everyone because it is now within the price range of most consumers and is mass produced in many variations
- Each retailer tries to persuade customers that its version of the style is the best
Stage 4 - decline
- The fourth stage of the cycle when the market is saturated and popularity decreases
- The fashion is overused and becomes dull and boring
- As the fashion decreases in popularity, retailers mark down their prices
- Promotions centre around major clearance or closeout sales of the fashion
Stage 5 - obsolescence
- The fifth stage of the cycle when the style is rejected, is undesirable at any price, Is no longer worn, no Longer produced
- Ends as an accepted fashion
- Extensions and renewal of brand, try to target new audiences
Extension strategy
- Can be defined as - a medium to long term plan for lengthening a products life cycle It is likely to be implemented during the maturity or early decline
- Extension strategies include
- Redesigning the product - new and improved
- Adding an extra feature now with … (colour , quality, texture )
- Changing the packaging and advertising to appeal to a new market segment
- Providing a unique selling point ( USP)


Comments
Post a Comment